Variables:
- #Variables in R serve as containers to store values. R primarily utilizes five main variable types: Integer, Double, Complex, Character, and Logical.
- In R, the assignment operator “<-” is used to assign a value to a variable.
- integer(non-decimal numbers) , we use L with the value.
- a<- 2L
- typeof( a) # to check the type of datatype is the value assigned
- Double(decimal number) , by default R uses this.
- b <- 2.5
- typeof ( b)
- Complex
- c <- 2+3i
- typeof( c)
- Character( for strings/ letters), always use quotes to write strings
- d <- “Hi”
- typeof (d)
- Logical : TRUE or FALSE or use T or F
- e <- TRUE
- typeof(e)

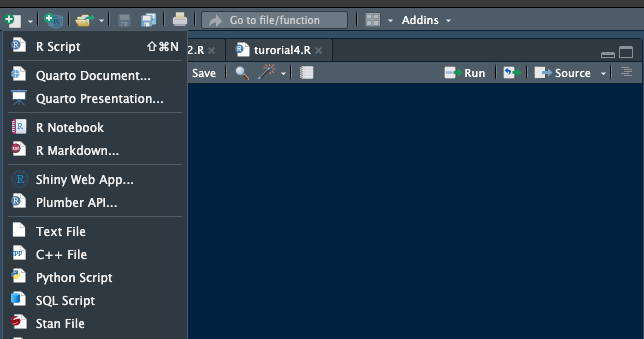
- Next, ensure to save your R script to prevent any loss of work. To create a new script for additional coding, click on the “+” button located at the top left corner of R Studio and select “R Script.”
- To reset and clear the environment, click on the broom button located in the Environment section. This action allows you to start with a fresh workspace.
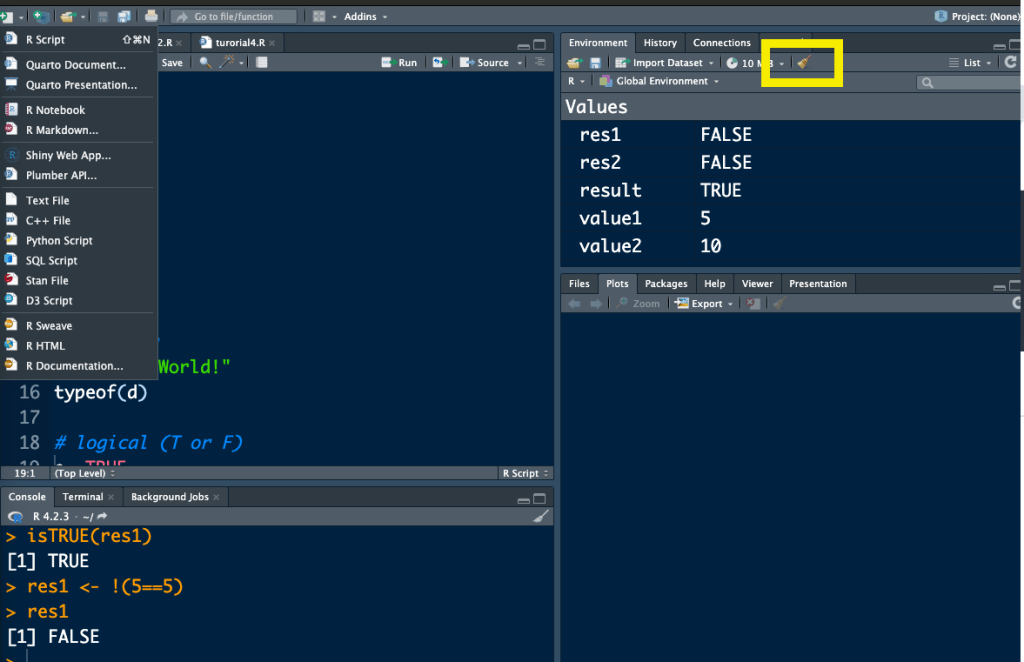
To execute the code in R Studio
- In contrast to other programming languages where commands like “Print” or “printf” are used to execute the program.
- In R, executing the program is as simple as calling the object in the next line of code.
Eg : Var1 <- 5
Var2 <- 10
Var <- Var1 + Var2
Var # to execute the code

Leave a comment