Predicting whether a loan application will be approved or rejected is a critical task for financial institutions. In this blog, we’ll walk through a hands-on machine learning exercise to build a loan status prediction model using real-world data. By the end, you’ll understand how to clean the data, select the right features, and train a model that can help automate loan decisions with accuracy and confidence.
workflow: data > data pre processing > split the data into train test split > SVM( supervised learning :Machine learning model)
new data > trained support vector machine model > approved or rejected
Import the dependencies
- import numpy as np
- import pandas as pd
- import seaborn as sns
- from sklearn import svm
- from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
- from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
Data Collection and Data Preprocessing
- #loading the dataset to pandas dataframe
- loan_dataset =pd.read_csv(‘/content/loan_dataset.csv’)
- type(loan_dataset)
link to practice the dataset :
https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/altruistdelhite04/loan-prediction-problem-dataset
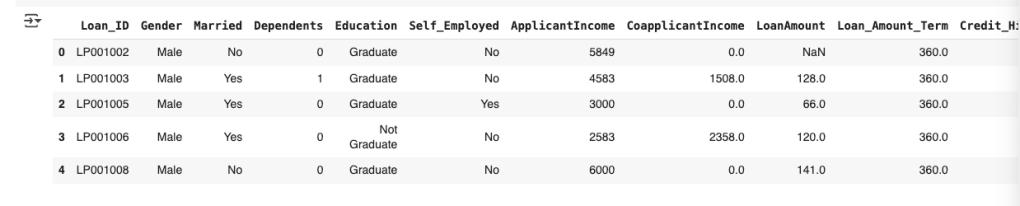
- # printing the first 5 rows of the dataframe
- loan_dataset.head()
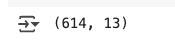
- # no of rows and columns
- loan_dataset.shape
- # statistical measures
- loan_dataset.describe()

- # number of missing values in each column
- loan_dataset.isnull().sum()

- # dropping the missing values
- loan_dataset = loan_dataset.dropna()
- loan_dataset.isnull().sum()

label encoding
loan_dataset.replace({“Loan_Status”:{‘N’:0,’Y’:1}},inplace=True)
loan_dataset.head()
- # dependent column values
- loan_dataset[‘Dependents’].value_counts()

- # replacing the value of 3+ to 4
- loan_dataset = loan_dataset.replace(to_replace=’3+’, value=4)
- # dependent values
- loan_dataset[‘Dependents’].value_counts()

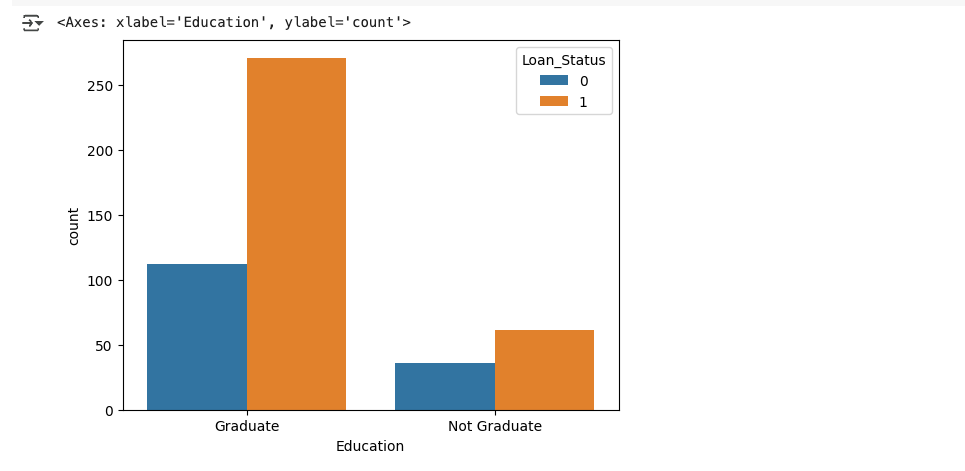
Data Visualisation
- # education and loan status
- sns.countplot(x=’Education’,hue=’Loan_Status’,data = loan_dataset)
- # married and loan status
- sns.countplot(x=’Married’,hue=’Loan_Status’,data = loan_dataset)

- # convert categorical data into numerical data
- loan_dataset.replace({‘Married’:{‘No’:0,’Yes’:1},’Gender’:{‘Male’:1,’Female’:0},’Self_Employed’:{‘No’:0,’Yes’:1},’Property_Area’:{‘Rural’:0,’Semiurban’:1,’Urban’:2},’Education’:{‘Graduate’:1,’Not Graduate’:0}},inplace=True)
- loan_dataset.head()
- # separating the data and label
- X = loan_dataset.drop(columns=[‘Loan_ID’,’Loan_Status’],axis=1)
- Y = loan_dataset[‘Loan_Status’]
- print(x)
- print(y)

Train Test Split
- X_train, X_test,Y_train,Y_test = train_test_split(X,Y,test_size=0.1,stratify=Y,random_state=2)
- print(X.shape, X_train.shape, X_test.shape)

Training the model : Support Vector Machine
- classifier = svm.SVC(kernel=’linear’)
- #training the support Vector Macine model
- classifier.fit(X_train,Y_train)

Model evaluation
- # accuracy score on training data
- X_train_prediction = classifier.predict(X_train)
- training_data_accuray = accuracy_score(X_train_prediction,Y_train)
- print(‘Accuracy on training data : ‘, training_data_accuray)

- # accuracy score on testing data
- X_test_prediction = classifier.predict(X_test)
- test_data_accuracy = accuracy_score(X_test_prediction,Y_test)
- print(‘Accuracy on testing data : ‘, training_data_accuracy)

Making a predictive system
- input_data = (1,1,1,1,0,4583,1508.0,128.0,360.0,1.0,0)
- # changing the input_data to numpy array
- input_data_as_numpy_array = np.asarray(input_data)
- # reshape the array as we are predicting for one instance
- input_data_reshaped = input_data_as_numpy_array.reshape(1,-1)
- # standardize the input data
- # scaler.transform(input_data_reshaped)
- prediction = classifier.predict(input_data_reshaped)
- print(prediction)
- if (prediction[0] == 0):
- print(‘The person is not eligible for loan’)
- else:
- print(‘The person is eligible for loan’)

Disclaimer: All information provided on www.academicbrainsolutions.com is for general educational purposes only. While we strive to provide accurate and up-to-date information, we make no representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, about the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability, or availability of the information contained on the blog/website for any purpose. Any reliance you place on such information is therefore strictly at your own risk. The information provided on www.academicbrainsolutions.com is not intended to be a substitute for professional educational advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your qualified educational institution, teacher, or other qualified professional with any questions you may have regarding a particular subject or educational matter. In no event will we be liable for any loss or damage including without limitation, indirect or consequential loss or damage, or any loss or damage whatsoever arising from loss of data or profits arising out of, or in connection with, the use of this blog/website. Our blog/website may contain links to external websites that are not provided or maintained by us. We do not guarantee the accuracy, relevance, timeliness, or completeness of any information on these external websites. Comments are welcome and encouraged on www.academicbrainsolutions.com is but please note that we reserve the right to edit or delete any comments submitted to this blog/website without notice due to: Comments deemed to be spam or questionable spam, Comments including profanity, Comments containing language or concepts that could be deemed offensive, Comments that attack a person individually.By using www.academicbrainsolutions.com you hereby consent to our disclaimer and agree to its terms. This disclaimer is subject to change at any time without prior notice
Leave a comment